|
 |
| DOCUMENTATION |
| FLEXIBLE METADATA STORING - ELSEM REPORT - |
| - Introduction |
| - Storage alternatives for semantic metadata |
| - OpenCyc |
| - Overall description of the SLOR prototype |
| - Integrating the large commonsense ontology |
| - Problems found |
| - Final Proposed Architecture |
| DOWNLOAD |
| WORKING GROUP |
| Further Work |
| Overall description of the SLOR prototype |
|
The SLOR prototype has been specifically designed for the creation
and management of learning object metadata with integration and exchange
purposes. In order to maintain the consistency between the different
layers, the SLOR prototype uses the ontology described in (Soto, Sánchez-Alonso
and Sicilia). Functionalities are grouped in modules, following the
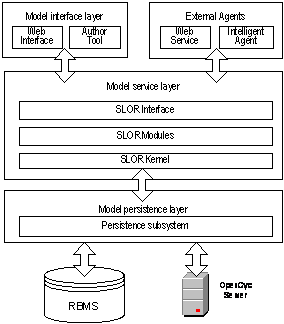
scalability design principle. Figure [6] depicts the main layers and
technologies of the prototype architecture, as an illustration of
a semantic-enabled learning object repository:
- The interface layer allows the access from different tools to the SLOR functions. Thus a web interface can be connected to SLOR over the HTTP protocol, and also author tools can connected through web services protocols. Furthermore the layer interface will provide a new set of interfaces thus enabling federation between different repositories. - The model service layer provides transparent access to different functionalities of the semantic learning object repository. The SLOR interface defines a protocol of behaviour between this layer and the actions of the user interface. This interface separates the GUI from the SLOR services. The design principles of SLOR interface are based in metadata actions, implemented in modules that enable learning objects accessibility, interoperability, durability and reusability. This interface receives requests from either the Web interface or other agents using the SLOR ontology. These queries are in turn routed to the appropriate module in the following layer. The SLOR modules provide a scalable architecture to easily add new functionalities. Herein, a modular scalable architecture for expanding system functionalities through continued addition of modules is proposed, with the aim of advancing towards a standard architecture for SLOR. In order to include all the functionalities related to the creation, deletion and updating of reusable learning objects, a management module has been implemented. - The SLOR kernel provides a middleware with basic functions for operating the ontology model. Examples of functions provided by this kernel are: getIndividuals (retrieves all the individuals of a given class in the repository) or setMultipleProperty (inserts all the objects in a list as the values of a multiple property of an instance). In order to provide flexibility in the change of a semantic web framework and evaluate the performance offered by these, layer establishes a common interface to SLOR basic functions using the abstract factory pattern. - A Semantic Web Framework is used to handle at low-level the OWL ontology model. The persistence of the underlying ontological model is stored on a relational database system, using the built-in persistence capabilities of the Semantic Web framework (such as Jena or Sesame).
|